Good Quality Chery J2 - air conditioner condenser part for chery – Qingzhi
Good Quality Chery J2 - air conditioner condenser part for chery – Qingzhi Detail:
| Product name | Air conditioner condenser |
| Country of origin | China |
| Package | Chery packaging, neutral packaging or your own packaging |
| Warranty | 1 year |
| MOQ | 10 sets |
| Application | Chery car parts |
| Sample order | support |
| port | Any Chinese port,wuhu or shanghai is best |
| Supply Capacity | 30000sets/months |
Condenser is a component of refrigeration system and belongs to a kind of heat exchanger. It can convert gas or vapor into liquid and transfer the heat of refrigerant in the pipe to the air near the pipe. (the evaporator in automobile air conditioner is also a heat exchanger)
Function of condenser:
Heat and cool the high-temperature and high-pressure gaseous refrigerant discharged from the compressor to condense it into medium temperature and high-pressure liquid refrigerant.
(Note: almost 100% of the refrigerant entering the condenser is gaseous, but it is not 100% liquid when leaving the condenser. Because only a certain amount of heat can be discharged from the condenser within a given time, a small amount of refrigerant will leave the condenser in gaseous form. However, since these refrigerants will enter the receiver dryer, this phenomenon will not affect the operation of the system.)
Exothermic process of refrigerant in condenser:
There are three stages: overheating, condensation and supercooling
1. The refrigerant entering the condenser is a high-pressure superheated gas. Firstly, it is cooled to the saturation temperature under the condensation pressure. At this time, the refrigerant is still gaseous.
2. Then, under the action of condensation pressure, release heat and gradually condense into liquid. In this process, the refrigerant temperature remains unchanged.
(Note: why does the temperature remain unchanged? This is similar to the process of solid turning into liquid. Solid turning into liquid needs to absorb heat, but the temperature does not rise, because all the heat absorbed by solid is used to break the binding energy between solid molecules.
In the same way, if the gaseous state becomes liquid, it needs to release heat and reduce the potential energy between molecules.)
3. Finally, continue to release heat, and the temperature of liquid refrigerant decreases to become supercooled liquid.
Types of automobile condenser:
There are three types of automobile air conditioning condensers: segment type, pipe belt type and parallel flow type.
1. Tubular condenser
The tubular condenser is the most traditional and earliest condenser. It is composed of aluminum heat sink with thickness of 0.1 ~ 0.2mm sleeved on the round pipe (copper or aluminum). The pipe is expanded by mechanical or hydraulic methods to fix the heat sink on the round pipe and close to the pipe wall, so as to ensure that the heat can be transmitted through the close fitting pipe.
Features: large volume, poor heat transfer efficiency, simple structure, but low processing cost.
2. Tube and belt condenser
Generally, the small flat tube is bent into a snake tube shape, in which triangular fins or other types of radiator fins are placed. As shown in the figure below.
Features: its heat transfer efficiency is 15% ~ 20% higher than that of the tubular type.
3. Parallel flow condenser
It is a tube belt structure, which is composed of cylindrical throttle tube, aluminum inner rib tube, corrugated heat dissipation fin and connecting tube. It is a new condenser specially provided for R134a.
Features: its heat dissipation performance is 30% ~ 40% higher than that of tube belt type, the path resistance is reduced by 25% ~ 33%, the content product is reduced by about 20%, and its heat exchange performance is greatly improved.
Product detail pictures:
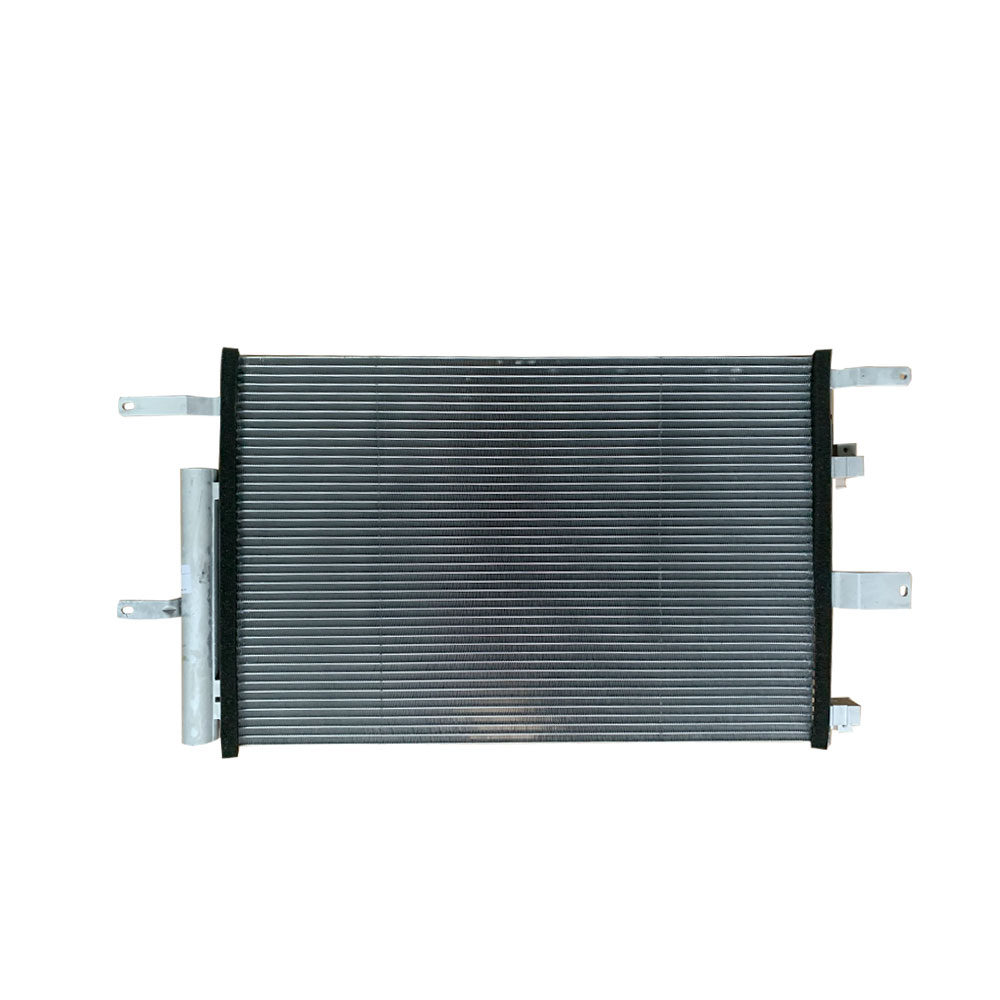
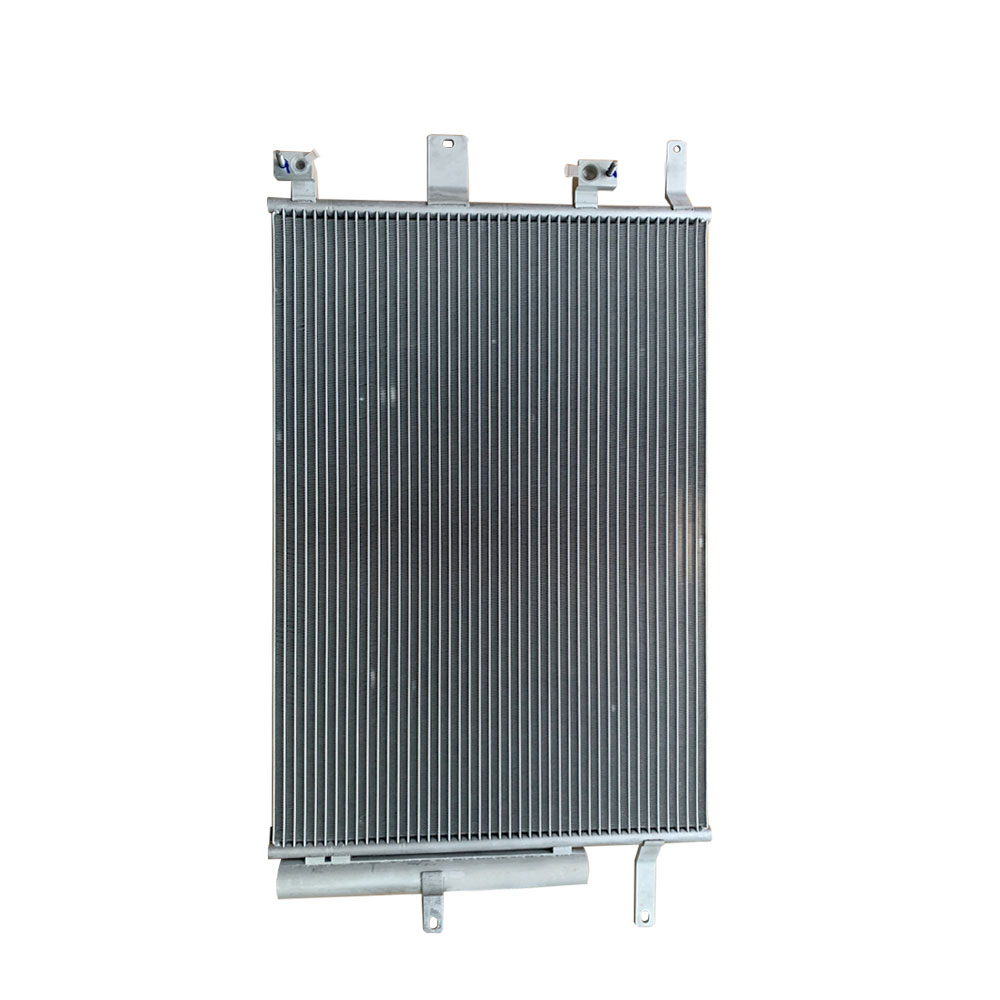


Related Product Guide:
In an effort to finest meet up with client's requirements, all of our operations are strictly performed in line with our motto "High High quality, Competitive Rate, Fast Service" for Good Quality Chery J2 - air conditioner condenser part for chery – Qingzhi , The product will supply to all over the world, such as: Ecuador , Lahore , Singapore , Corporate goal: Customers' satisfaction is our goal, and sincerely hope to establish long-terms stable cooperative relations with customers to jointly develop the market. Building brilliant tomorrow together!Our company regards "reasonable prices, efficient production time and good after-sales service" as our tenet. We hope to cooperate with more customers for mutual development and benefits. We welcome potential buyers to contact us.
Customer service staff and sales man are very patience and they all good at English, product's arrival is also very timely, a good supplier.