Good User Reputation for Chery Air Filter - ENGINE ACCESSORY COOLING SYSTEM for CHERY QQ SWEET S11 1.1L – Qingzhi
Good User Reputation for Chery Air Filter - ENGINE ACCESSORY COOLING SYSTEM for CHERY QQ SWEET S11 1.1L – Qingzhi Detail:
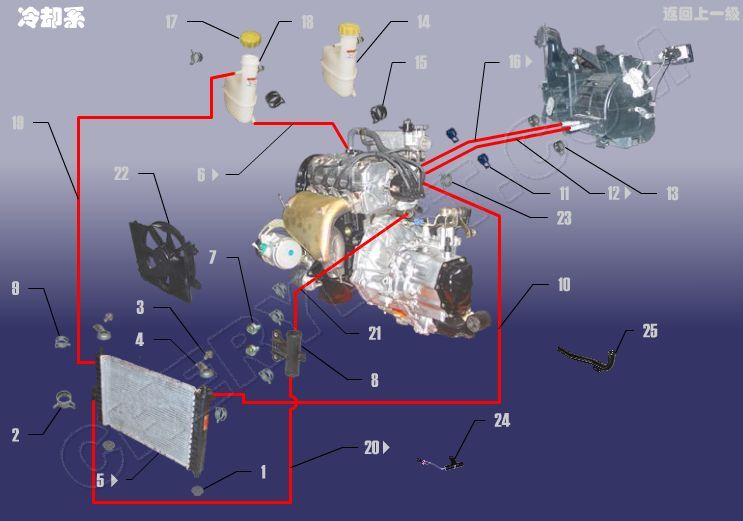
1 S11-1301313 SLEEVE,RUBBER
2 AQ60136 ELASTIC CLAMP
3 Q1840610 BOLT HEXAGON FLANGE
4 S11-1301311 RADIATOR TENSION PLATE
5 S11LQX-SRQ RADIATOR
6 S11SG-SG WATER PIPE-EXPANDING BOX TO COOLING WATER PIPE
7 Q1840820 BOLT HEXAGON FLANGE
8 S11-1303117 WATER INLET PIPE FIXING BRACKET
9 AQ60116 ELASTIC CLAMP
10 S11-1303211BA WATER OUTLET PIPE
11 AQ60122 ELASTIC CLAMP
12 S11NFJSG-NFJSG WARM-AIR BLOWER WATER INLET HOSE
13 AQ60124 ELASTIC CLAMP
14 S11-1311110 EXPANDING BOX ASSY
15 AQ60125 ELASTIC CLAMP
16 S11NFJCSG-NFJCSG HOSE,RADIATOR OUTLET
17 S11-1311120 EXPANDING BOX COVER ASSY
18 S11-1311130 EXPANDING BOX BODY ASSY
19 S11-1303313 WATER PIPE-RADIATOR TO EXPANDI
20 S11JSG?o-JSG?o WATER INLET PIPE II
21-1 S11-1303111BA PIPE,AIR INTAKE
21-2 S11-1303111CA HOSE – RADIATOR INLET
22 S11-1308010 FAN,RADIATOR
23 AQ60138 ELASTIC CLAMP
24 S11-1308035BA RESISTOR,SPEED-CHANGER
25 S11-1303310BA PIPE ASSY – WATER COOLING
Due to the congenital defect that the traditional coolant: water and aqueous antifreeze cannot meet the heat dissipation of the engine:
1. Water will freeze at 0 ℃ and boil at 100 ℃. Freezing will explode the engine water tank and cylinder block, and boiling will overheat the engine until it is paralyzed.
2. When the engine temperature reaches above 80 ℃, water bubbles should begin to appear on the cylinder wall. Water bubbles form a bubble heat barrier layer on the surface of the cylinder to prevent heat dissipation inside the engine. Water bubbles are generated and broken endlessly on the metal surface of the engine block, and the cylinder block is lost with the effect of dripping water through stone – this is cavitation.
3. The local temperature inside the engine is too high, the tendency of precombustion and detonation increases, increases vibration and noise, greatly reduces the engine performance and efficiency, and forms anhydrous fuel consumption.
4. The electrochemical corrosion of water under the action of electrolyte and the generation of rust and scale aggravate the aging speed of the cooling system and reduce the heat dissipation performance.
5. When the engine temperature reaches above 80 ℃, the water vapor, water bubbles and water expansion will increase the internal pressure of the cooling system. In this way, it not only catalyzes the aging speed of the cooling system, but also makes it gradually unable to ensure the speed required for normal heat dissipation due to corrosion. Therefore, the heat dissipation defects of aqueous antifreeze are summarized as follows: the heat dissipation performance is limited and can not hold the overheat peak; Gradually aging the engine, increasing the calorific value of the engine; Gradually aging the cooling system to reduce or increase the heat dissipation capacity.
Lack of liquid in the cooling system: the radiator is cracked, there is hole leakage or the cylinder water jacket is damaged, resulting in the outflow of cooling water; The water inlet and outlet pipes are damaged and leaking; The switch is damaged, resulting in liquid leakage.
Solution: stop the leakage of leakage liquid. If it is serious, replace the radiator; Replace the water inlet and outlet pipes; Replace the switch.
Too high engine coolant: too little cooling water; The power transmission belt of the fan is broken or too loose to give full play to its function; There is too much scale on the cylinder water jacket and radiator, which affects the heat dissipation performance; Abnormal operation of water pump leads to poor water circulation; The radiator fin is dumped or the connecting hose is sucked; One of the water temperature gauge and sensor fails or both fail.
Solution: add cooling water; Replace the drive belt or tighten the conveyor belt; Clean the cooling system; Repair the water pump; Check the water outlet pipe. If it is deflated, eliminate it and repair the radiator fins. Check the water temperature gauge and sensor.
Product detail pictures:
Related Product Guide:
We have probably the most state-of-the-art output equipment, experienced and qualified engineers and workers, recognized good quality manage systems plus a friendly skilled income workforce pre/after-sales support for Good User Reputation for Chery Air Filter - ENGINE ACCESSORY COOLING SYSTEM for CHERY QQ SWEET S11 1.1L – Qingzhi , The product will supply to all over the world, such as: Holland , Bangalore , Eindhoven , We welcome you to visit our company and factory. It is also convenient to visit our website. Our sales team will offer you the best service. If you need more information, please feel free to contact us by E-mail or telephone. We are sincerely hope to establish a good long-term business relationship with you through this opportunity, based on equal, mutual benefit from now till the future.
Company director has very rich management experience and strict attitude, sales staff are warm and cheerful, technical staff are professional and responsible,so we have no worry about product,a nice manufacturer.