Professional China Chery Qq Engine - Chassis STEERING SYSTEM STEERING COLUMN for CHERY AMULET A15 – Qingzhi
Professional China Chery Qq Engine - Chassis STEERING SYSTEM STEERING COLUMN for CHERY AMULET A15 – Qingzhi Detail:
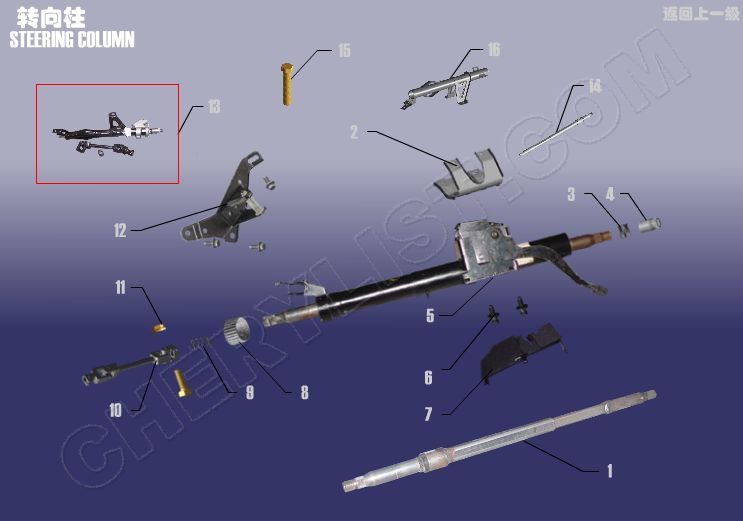
1 A11-3404110BB STEARING SHAFT ASSY
2 A11-3403101 STEERING TRAY
3 A11-3404037 PRESSURE SPRING
4 A11-3404035 TOOTHED SLEEVE
5 A11-3404001BA STEERING COLUMN WITH MAIN SHAFT
6 A11-3403103 SAFETY BOLT
7 A11-5305830 COVER SET COLUMN
8 A11-3404031 STEARING PILLAR LOWER BEARING
9 A11-3404039 PRESSURE SPRING-STEARING PILLA
10 A11-3404050BB POWER STEARING UNIVERSAL JOINT
11 CQ32608 HEXAGON HEAD FLANGE NUT
12 A11-3403030 STEARING PILLAR LOWER BRACKET
13 A11-3404010AB COLUMN and UNIVERSAL JOINT ASSY
14 A11-3404110 SHAFT ASSY – STEERING
15 CQ1600825 BOLT – FIXING STEERING GEAR
16 A11-3404100 COLUMN ASSY – STEERING
1. Function:
A special mechanism for changing or restoring the driving direction of a vehicle.
2. Composition:
Steering control mechanism
Steering gear
Steering transmission mechanism
3、 Steering system terminology
1. Steering center and turning radius
(1) Steering center: when the vehicle turns, all wheel axes are required to intersect at one point, which 0 is called the steering center.
(2) Turning radius: the distance r from the steering center 0 to the contact point between the outer steering wheel and the ground is called the turning radius of the vehicle
2. Steering trapezoid and forward spread
Inner corner of two steering wheels when turning β And outer corner α Difference β-α It is called forward exhibition. In order to produce forward spread, the steering mechanism is designed into trapezoid.
3. Steering system angular transmission ratio 1 Steering gear angular transmission ratio IW1:
The ratio of the steering wheel angle increment to the corresponding increment of the steering rocker arm angle. (2). Steering transmission ratio iw2:
The ratio of the angle increment of the steering rocker arm to the corresponding increment of the angle of the steering knuckle on the side where the steering wheel is located.
(3). Angular transmission ratio of steering system I: I = IW1 – I W2
The larger the angular transmission ratio of the steering system, the lighter the steering is. However, if the transmission ratio is too large, the steering control will not be sensitive enough.
4. Free stroke of steering wheel: the angular stroke of the steering wheel in the idling stage.
Excessive free travel: insensitive steering.
The free travel is too small: the road impact is large, and the driver is too nervous.
Product detail pictures:
Related Product Guide:
Adhering into the basic principle of "quality, assistance, effectiveness and growth", we have attained trusts and praises from domestic and worldwide client for Professional China Chery Qq Engine - Chassis STEERING SYSTEM STEERING COLUMN for CHERY AMULET A15 – Qingzhi , The product will supply to all over the world, such as: Ukraine , Canberra , Mexico , We care about every steps of our services, from factory selection, product development & design, price negotiation, inspection, shipping to aftermarket. Now we have implemented a strict and complete quality control system, which ensures that each product can meet quality requirements of customers. Besides, all of our solutions have been strictly inspected before shipment. Your Success, Our Glory: Our aim is to help customers realize their goals. We're making great efforts to achieve this win-win situation and sincerely welcome you to join us.
It's really lucky to find such a professional and responsible manufacturer, the product quality is good and delivery is timely, very nice.