Wholesale Discount Chery Hose - Engine IGNITION SYSTEM for CHERY AMULET A15 – Qingzhi
Wholesale Discount Chery Hose - Engine IGNITION SYSTEM for CHERY AMULET A15 – Qingzhi Detail:
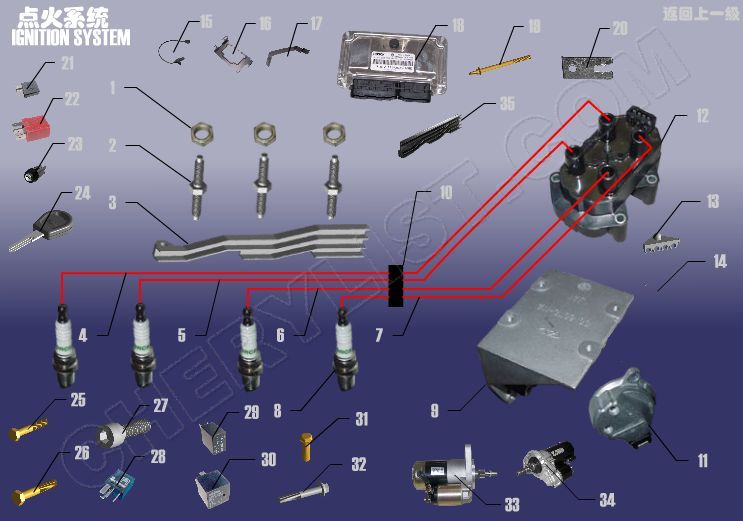
1 Q340B06 NUT – 1 SHAPED HEXAGON
2 480-1003074 STUD – EQUAL LENGTH
3 A11-3707177 CHANNEL – PROTECTING
4 A11-3707130EA CABLE – HIGH TENSION DISTRIBUTOR
5 A11-3707140EA CABLE – HIGH TENSION DISTRIBUTOR
6 A11-3707150EA CABLE – HIGH TENSION DISTRIBUTOR
7 A11-3707160EA CABLE – HIGH TENSION DISTRIBUTOR
8 A11-3707110BA PLUG ASSY – SPARK
9 A11-3705130 BRACKET – IGNITION COIL
10 A11-3707171 SUPPORT – HIGH TENSION CABLE
11 A11-3705120 SENSOR – PHRASE (IGNITION MODULE)
12 A11-3705110EA COIL – IGNITION
13 A11-3707173 SUPPORT – HIGH TENSION CABLE
14 A11-3724111 BAND
15 A11-1005120BA SENSOR – SPEED OF ROTATION
16 A11-3605015BE BRACKET – ECU
17 A11-3605019BE CLIP – SPRING
18 A11-BJ3605010BE ENGINE CONTROL UNIT
19 A11-3708111 STUD – HEXAGON
20 A11-3724861 BRACKET – CRANKSHAFT SENSOR
21 A11-3735047 RELAY – ECU
22 A11-3735049 RELAY
23 A11-8CB3704025 LOCK CYLINDER – IGNITION SWITCH
24 A11-8CB6105300 KEY – BLANK
25 CQ1601075 BOLT – HEXAGON HEAD
26 CQ1611035 BOLT – HEXAGON HEAD
27 CQ2180816 BOLT – INNER HEXGON HEAD
28 A11-3735051 RELAY
29 A11-3735052BA RELAY
30 A11-3735052BB RELAY
31 A11-1005203 BOLT – HEXAGON HEAD
32 Q1841060 BOLT – HEXAGON FLANGE
33 A11-3708110AD STARTER ASSY
34 A11-3708110 STARTER ASSY
35 A11-3707177BA CHANNEL – PROTECTING
1、 The function is to boost the low-voltage DC current to sufficient high voltage according to the working sequence of the engine (ignition sequence). Ignite the compressed high-temperature and high-pressure combustible mixture through the spark plug of each cylinder to complete the work process.
2、 The ignition system consists of battery, ignition switch, ignition coil, ignition control module, high-voltage wire, spark plug, etc.
3、 According to the control mode of primary circuit, the ignition system is divided into:
1. Traditional ignition system traditional ignition system is mainly composed of power supply (battery and generator), ignition switch, ignition coil, capacitor, breaker, distributor, spark plug, damping resistance and high-voltage wire. Working principle: turn on the ignition switch and the engine starts to run. The cam of the circuit breaker rotates continuously to make the contact of the circuit breaker open and close continuously. When the breaker contact is closed, the current of the battery starts from the positive pole of the battery and flows back to the negative pole of the battery through the ignition switch, the primary winding of the ignition coil, the movable contact arm of the breaker, the contact and the distributor housing. When the contact of the circuit breaker is pushed open by the cam, the primary circuit is cut off, the current in the primary winding of the ignition coil rapidly drops to zero, and the magnetic field around the coil and in the iron core also rapidly attenuates or disappears. Therefore, induced voltage is generated in the secondary winding of the ignition coil, which is called secondary voltage. The current passing through is called secondary current, and the circuit through which the secondary current flows is called secondary circuit. After contact disconnection, the higher the decline rate of primary current, the greater the change rate of magnetic flux in the core, and the higher the induced voltage generated in the secondary winding, the easier it is to break through the spark plug gap. When the magnetic flux in the core of the ignition coil changes, high voltage (mutual inductance voltage) is generated not only in the secondary winding, but also in the primary winding. When the contact is separated and the primary current drops, the direction of the self induced current is the same as that of the original primary current, and its voltage is as high as 300V. It will break through the contact gap and produce strong electric sparks between the contacts, which not only makes the contacts oxidize and ablate rapidly and affects the normal operation of the breaker, but also reduces the change rate of the primary current, the induced voltage in the secondary winding and the spark in the spark plug gap, so that it is difficult to ignite the mixture. In order to eliminate the adverse effects of self induced voltage and current, a capacitor C1 is connected in parallel between the breaker contacts. At the moment of contact separation, the self induced current charges the capacitor, which can reduce the spark between contacts, accelerate the attenuation of primary current and magnetic flux, and increase the secondary voltage.
2. Electronic ignition system
3. Microcomputer controlled ignition system
Product detail pictures:
Related Product Guide:
We are commitment to offer the competitive price ,outstanding products quality, as well as fast delivery for Wholesale Discount Chery Hose - Engine IGNITION SYSTEM for CHERY AMULET A15 – Qingzhi , The product will supply to all over the world, such as: Vancouver , Dubai , Salt Lake City , During in 11 years, We have participated in more than 20 exhibitions, obtains the highest praise from each customer. Our company has been devoting that "customer first" and committed to helping customers expand their business, so that they become the Big Boss !
Factory equipment is advanced in the industry and the product is fine workmanship, moreover the price is very cheap, value for money!